Protecting Archaeological Monuments
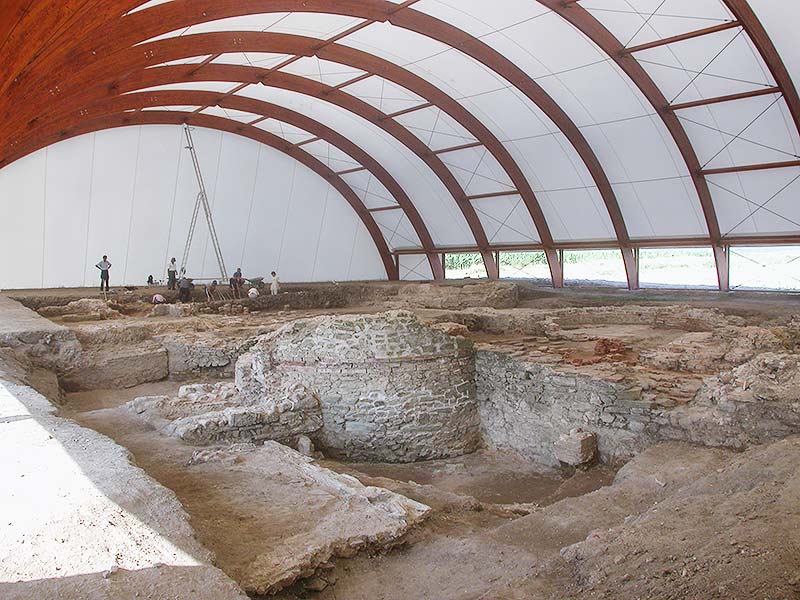
The Viminacium project has introduced a very important protective measure that concerns the future of archaeological monuments and sites. The explored structures, such as the baths (thermae), the north gate and the mausoleum are covered with a kind of roof and presented as objects of interest for tourists. The roofing consists of a light lamellar structure and a special covering sheet. The use of these materials makes it possible to bridge large spans without any support in the monument itself. What is especially important, the setting up of such roofing structures does not involve any damage to the archaeological layers. The north gate of the military camp, i.e. the castrum, and the baths are covered with transparent sheets made of a special material and have curtains designed in such a way as to provide good ventilation in the summer months.
The mausoleum is pyramidal in shape and it will be covered with polycarbonates, so that it has already been given the working name “The Crystal Mausoleum”. At present, it is covered with a structure of light wood and French awning. It is one of the most representative archaeological monuments in this part of Europe and certainly one of the finest in Serbia.
THE MAUSOLEUM – the protective covering and other structures
The roofing above the mausoleum consists of supports made of bonded lamellate wood (LLD). The basic structure has eight curved and four straight LLD supports. The other elements of the wooden structure are made of bonded lamellate and solid wood, while the metal structure is anchored between the LLD supports. The LLD supports are joined by screws. The elements of solid wood which form the pyramidal apex of the structure are joined by metal connecters.
The curved supports have a span of 20 meters and their base is in the form of a square with rounded angles. The structure covers an area of 32 x 32 meters.
The structure rests on concrete foundation walls, which enclose the area underneath the structure. The area of the cemetery is square in form and has several concrete extensions for the graves of large dimensions.
The roofing follows the form of the space it covers. The biggest, central grave in the cemetery is lit directly through the top part of the structure. Thus the covering structure itself highlights the central spot in the cemetery. Such protective structures made of bonded lamellate wood are not aesthetically inferior to those made of steel and glass, and they are increasingly replacing the more expensive traditional roofing structures made of solid wood. In conclusion, it can be said that the large span and the materials of this construction impart elegance and warmth to the site and enhance the sense of solemnity and awe which this monument evokes.
Gallery